Your Guide to the Future of Smart Warehousing

The warehousing industry is at a crossroads. Traditional facilities optimized for bulk storage and distribution struggle to meet the demands of on-demand, e-commerce fulfillment. Faster delivery expectations and order complexity require a more streamlined approach. This has led to the rise of smart warehousing – an intelligent approach to fulfillment that leverages advanced technologies and data to optimize how goods are stored, picked, packed, and shipped.
Continue reading to explore how smart warehouses use automation and technology to augment human capabilities and address evolving logistics challenges. Plus, get access to our guide to warehouse augmented reality. We’ll examine the current state of modern warehousing and innovative strategies for increasing efficiency, resilience, and competitiveness.
IN THIS ARTICLE
The State of Smart Warehousing
Challenges of Smart Warehousing
Smart Warehousing Technologies
The Human Element in Smart Warehousing
The Future of Smart Warehousing
What is a Smart Warehouse?
A smart warehouse is a fulfillment center that uses advanced technologies and automated systems to optimize how goods are stored, picked, packed, and shipped. These intelligent facilities create a data-driven ecosystem of interconnected technologies that work with employees to streamline processes, reduce errors, and boost efficiency
Imagine:
- Warehouse management systems (WMS) communicating with autonomous mobile robots to streamline the movement of goods through the warehouse
- Sensors providing real-time data on inventory levels
- Augmented intelligence guiding workers through complex tasks
This modern approach to warehouse management is the culmination of years of innovation. Let’s look at how warehousing has transformed throughout history, paving the way for today’s smart warehouses.
The Rise of E-Commerce and Smart Warehousing
The rise of online shopping transformed consumer expectations around delivery times. Speedy delivery became the new standard, putting pressure on warehouses to adapt. Fulfilling high volumes of individual online orders quickly and accurately required warehouses to shift from managing large, bulk shipments to a just-in-time approach prioritizing individual items. Warehouses began leveraging automation to augment human capabilities and optimize efficiency.
As e-commerce continues to grow, its impact on warehousing is profound. According to CBRE, the U.S. e-commerce market is expected to reach 26% of all retail sales by 2025, which will require an added 330 million square feet of warehousing and distribution space.
The State of Smart Warehousing
As e-commerce flourishes, it’s not just warehouses facing challenges. The entire supply chain, from sourcing materials to delivering finished products, is pressured to adapt. Manufacturers need to improve production processes to meet tighter deadlines. Warehouses and distributors require flexible storage and fulfillment solutions to accommodate a wider variety of products and fulfill high order volumes quickly and accurately.
These pressures create unique challenges for modern warehouses, but they also present exciting opportunities.
Challenges of Smart Warehousing

As critical components of integrated supply chains, warehouses face numerous challenges. These challenges test the resilience and adaptability of warehousing operations and drive ongoing evolution towards smarter, more responsive facilities.
- Labor shortages: Finding and retaining qualified workers for physically demanding warehouse jobs is a growing concern. Employee turnover rates in warehouses can be as high as 35%. The reliance on temporary and seasonal labor creates inconsistency and the need to quickly onboard new hires adds pressure to reduce training time.
- Increasing order volumes and SKUs: A surge in e-commerce orders is pressuring warehouses to expand inventory and fulfill more orders in less time.
- High customer expectations around delivery timelines: Customers expect faster deliveries, wider selection, and real-time order tracking. In fact, 56% of shoppers aged 18-34 expect same-day delivery. This places pressure on warehouses to increase the speed of order processing and delivery.
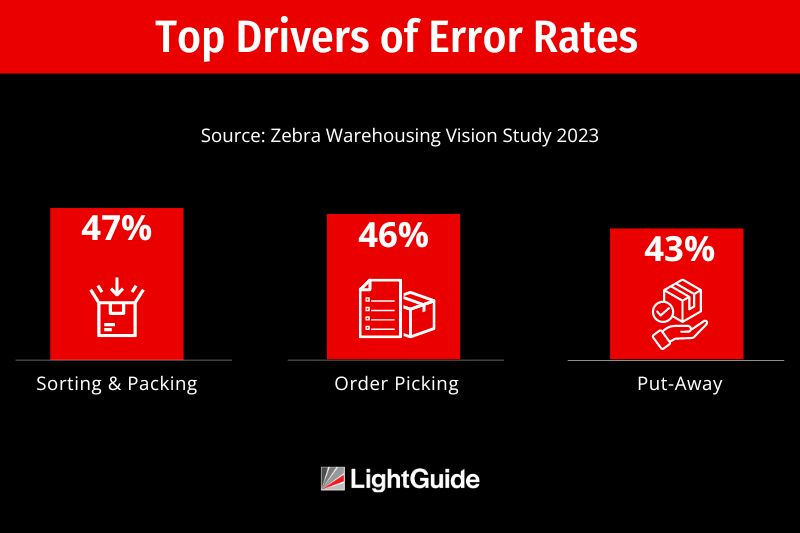
- Order picking accuracy: Mistakes can lead to returns, customer dissatisfaction, and increased costs.
- Inventory management: Inaccurate inventory data can cause stockouts, delays, and unhappy customers.
- Heightened competition: The rise of e-commerce has intensified competition, with businesses vying for customer loyalty through faster fulfillment times and lower costs.
Smart Warehousing Strategies Transforming Challenges into Opportunities
As e-commerce evolves and customer expectations for rapid delivery intensify, warehouses must innovate and adapt. Escalating order volumes, lightning-fast delivery expectations, and a growing scarcity of skilled labor are just some of the challenges modern warehouses must navigate.
Meeting these demands requires peak efficiency and accuracy. However, traditional warehouse methods often struggle to keep pace with the increasing pressure for faster fulfillment.
- Slow picking and packing processes lead to delays
- Picking errors frustrate customers and generate returns
- Repetitive tasks and heavy lifting cause workplace injuries
- Inefficient space utilization wastes valuable storage capacity
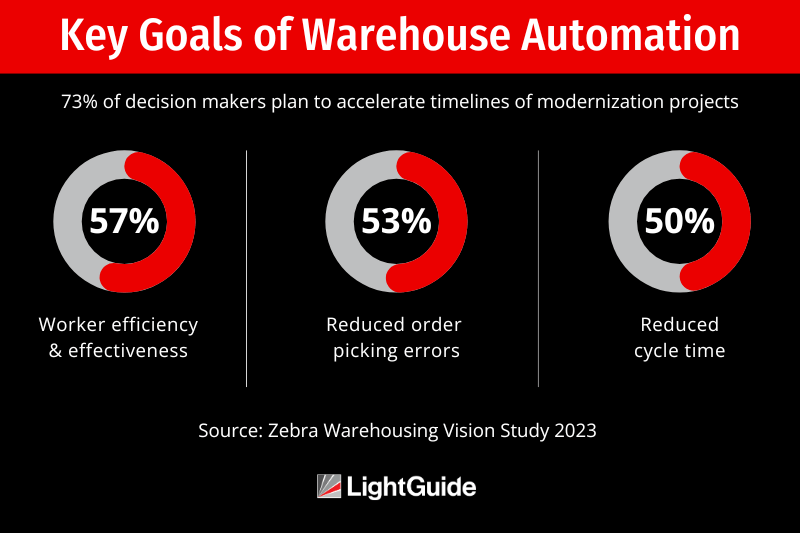
To address these challenges and increase efficiency, warehouse leaders are accelerating investments in technology to modernize operations and enhance human capabilities. According to Zebra Technologies’ Warehousing Vision Study, 80% of decision-makers agree that investing in new technology is essential over the next five years. They believe enhancing speed, accuracy, and labor optimization is crucial to keeping up with e-commerce demands and ensuring competitiveness in an on-demand economy.
Let’s explore some smart warehousing strategies companies use to improve intralogistics and boost efficiency.
RELATED ARTICLE: How to Improve Intralogistics in the Age of Smart Warehousing
Harness the Power of Automation
In today’s fast-paced e-commerce environment, automation plays a crucial role in streamlining warehouse operations and boosting efficiency. Smart warehouses are increasingly turning to automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), sortation systems, and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to manage the complexity of increasing order volumes.
Although more than 80% of warehouses currently lack automation solutions, investment in this technology is accelerating. According to Supply & Demand Chain Executive, many industry experts believe we will start to see an increase in adoption over the next five years. Furthermore, projections from Research and Markets show that the warehouse automation technology market could grow to $37.6 billion by 2030.
Engage in Strategic Workforce Planning
Automation doesn’t eliminate the need for human workers, it simply changes the types of roles needed. Strategic workforce planning is crucial for optimizing the human element in smart warehouses. Data-driven insights gathered from IoT devices and workforce management software allow warehouse managers to:
- Better forecast labor demands
- Align staffing levels with operational requirements
- Pinpoint tasks best suited for automation so workers focus on higher-value activities
Augment Human Capabilities with Technology
While automation excels at repetitive tasks, human workers continue to play a crucial role in smart warehousing. Technology can be used to augment human capabilities, leading to a more productive and error-free work environment.
In fact, 77% of respondents in Zebra Technologies’ Warehousing Vision Study agree that the best way to introduce automation is by augmenting workers with technology. For example, augmented reality (AR) and wearable technologies provide hands-free access to real-time information, guiding workers to the correct item locations, reducing picking errors, and streamlining workflows.
RELATED ARTICLE: Warehouse AR: How Augmented Reality is Transforming Logistics

Invest in Upskilling and Reskilling Programs
Investing in training equips employees with the skills necessary to operate and maintain automation technologies. Cross-training allows workers to perform various tasks within the warehouse, increasing flexibility and ensuring operational continuity even during staffing shortages.
Improve Agility for Market Fluctuations
The e-commerce landscape is constantly evolving, and warehouses need to be adaptable. With the help of smart warehousing solutions, organizations can dynamically adapt to market fluctuations.
Real-time data, enabled by warehouse management systems (WMS) and other smart warehousing technologies, facilitate quick decision-making. This allows warehouses to respond proactively to changing demand patterns, supply chain disruptions, or urgent orders.
By adopting these smart warehousing strategies, companies can meet today’s demands while positioning themselves for future growth.
Smart Warehousing Technologies Transforming Logistics
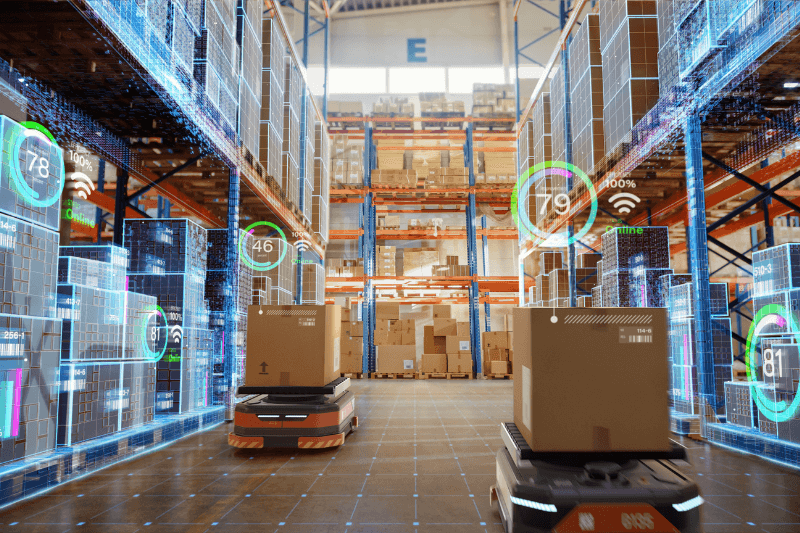

Smart warehouses leverage a range of technologies to address operational challenges. Warehouse automation and robotics, working alongside augmented intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT), streamline processes, minimize errors, and optimize material handling. Let’s explore some of the key technologies revolutionizing the future of smart warehousing.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
A warehouse management system acts like the brain of a smart warehouse, overseeing and streamlining all aspects of warehouse operations. These systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, order fulfillment status, and resource allocation. They tell robots where to go, improve picking routes, and ensure there’s always enough inventory on hand.
- Warehouse operations management: The WMS manages the flow of goods from receiving to picking, packing, and shipping. This includes generating pick lists and shipping labels and tracking the location of inventory within the warehouse.
- Labor management: The WMS can assign tasks to warehouse workers based on workload and demand forecasts. It can also track worker performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Space optimization: The system helps optimize warehouse layout by suggesting the best storage locations for different items based on size, weight, and frequency of access. This helps maximize storage capacity and streamline picking routes.
- Integration with other systems: A WMS can also integrate with other systems, such as digital and AR work instructions, wearable barcode scanners, and automated robotics systems.
- Reporting and analytics: The WMS provides valuable reports on warehouse performance metrics such as picking accuracy, order fulfillment times, and warehouse space utilization. These reports help identify areas for improvement and optimize warehouse operations.
Inventory Management Systems (IMS)
Inventory management systems leverage real-time data to ensure the right inventory is always on hand.
- Stock level tracking: The IMS keeps a real-time record of the quantity of each item in the warehouse. This allows for better visibility into inventory levels and helps avoid stockouts or overstocking.
- Demand forecasting: The system can analyze historical sales data and identify trends to predict future demand for specific products. This information ensures sufficient stock while avoiding the unnecessary cost of holding excess inventory, thereby freeing up valuable warehouse space and capital.
- Reorder point management: The IMS can calculate reorder points – the minimum stock level at which a new order needs to be placed to avoid stockouts. This helps maintain optimal inventory levels and prevent disruptions in the fulfillment process.
- Inventory valuation and costing: The system can also track the cost of goods and help calculate the value of the inventory at any given time.
- Inventory reporting and analytics: An IMS can generate reports on various aspects of inventory, such as stock movement trends, product popularity, and inventory turnover rates.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) enhances warehouse operations by creating a network of interconnected devices and sensors that collect and share data to enable automation and optimize intralogistics processes for greater efficiency.
IoT serves as a bridge connecting various digital systems within the warehouse, including everything from warehouse management systems and sensors on shelves to wearable devices. This connectivity ensures data flows seamlessly between systems, enabling more coordinated and data-driven decision-making.
Here are some other pivotal capabilities IoT enables in a warehouse setting:
- Real-time inventory management: IoT devices such as RFID tags and sensors are attached to inventory items, pallets, or shelves. This allows for real-time tracking of stock levels and locations. For instance, smart shelves equipped with weight sensors can automatically reorder stock when levels are low.
- Environmental condition monitoring: Sensors embedded in storage areas can monitor conditions that affect product quality, such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure. This is particularly crucial in warehouses that store sensitive items like food, pharmaceuticals, or chemicals.
- Improved asset tracking and utilization: IoT technology also tracks the equipment and vehicles used within the warehouse, such as forklifts and automated mobile robots. By monitoring the usage and condition of these assets in real time, smart warehouses can optimize their deployment, schedule maintenance more effectively, and reduce downtime.
- Enhanced worker safety: Wearable sensors can monitor worker location and activity in relation to robots, helping to identify potential safety hazards.
- Predictive maintenance: By collecting and analyzing data from machinery and equipment, IoT devices can predict when maintenance is needed. This helps smart warehouses avoid unexpected breakdowns and maintain continuous operations.
Big Data, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Machine Learning (ML)
Data is the lifeblood of smart warehousing. Sensors and IoT devices generate real-time data on inventory levels, equipment performance, and worker activity. AI analyzes this data to predict trends, optimize picking routes, and manage resources more effectively. Machine learning algorithms continuously learn from data and identify areas for improvement.
- Demand forecasting anticipates inventory needs and prevents stockouts
- AI optimizes picking routes and warehouse layouts for maximum efficiency
- Real-time data from sensors track the location and movement of goods
- Interactive dashboards and visual displays empower workers with real-time data on inventory levels and order fulfillment status
Warehouse Automation and Robotics Technologies
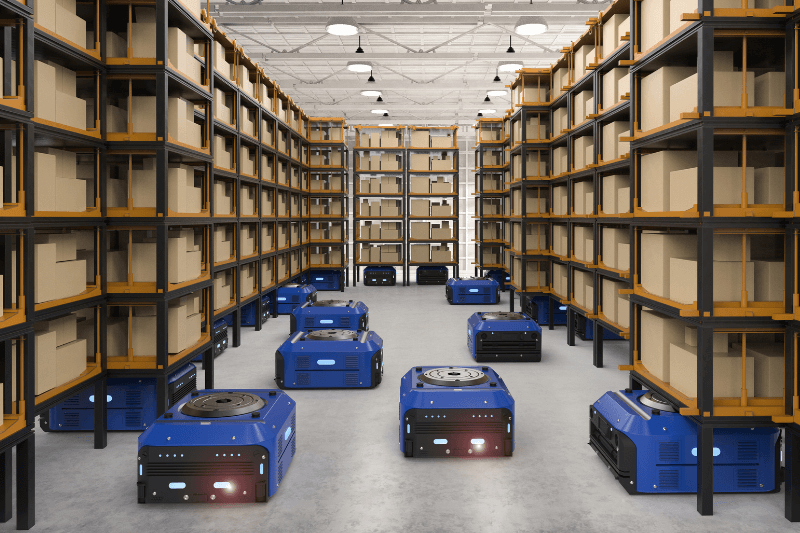

The rise of e-commerce and the ever-increasing demand for faster fulfillment have fueled the rapid adoption of warehouse automation technologies. These technologies come in various forms, each addressing specific intralogistics needs. Some key examples of automation and robotics technologies used in smart warehouses include:
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
Automated storage and retrieval systems are a key technology used in smart warehouses. These systems typically work under the control of a warehouse management system and use robots and computer-controlled mechanisms to store and retrieve goods.
In smart warehouses, AS/RS are often integrated with other automated solutions like automated guided vehicles, autonomous mobile robots, and advanced conveyor systems that transport items to and from the AS/RS. This integration allows for a seamless flow of goods through the warehouse, minimizing delays and bottlenecks.
By maximizing storage density, these systems significantly reduce floor space required, allowing for speedy item retrieval, storage, and ultimately, faster fulfillment.
Automated Guided Vehicles and Autonomous Mobile Robots
Automated guided vehicles and autonomous mobile robots are the workhorses of modern smart warehouses, playing a critical role in material handling processes.
The increasing demand for efficiency and productivity, particularly in the age of e-commerce, is fueling the rapid adoption of these robots. In fact, automated guided vehicles and autonomous mobile robots are expected to be a significant force in warehouse automation, making up close to a quarter of the 4 million commercial warehouse robots projected to be installed by 2027.
Automated guided vehicles and autonomous mobile robots improve efficiency and productivity by automating the internal transport of goods. This speeds up material handling, reduces transit times, and allows human workers to focus on more complex tasks.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs predefined paths in a warehouse using physical guidance systems or markers to navigate their environment. This makes them highly predictable and reliable for repetitive tasks. They are typically used to transport heavy loads across large facilities. Common uses include transporting raw materials to production lines, moving products to storage areas, or taking finished goods to shipping docks.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
AMRs are self-navigating robots that can efficiently transport goods within the warehouse. Unlike AGVs, AMRs don’t need predefined paths to navigate a warehouse. They use sensors, cameras, and mapping technologies to navigate the warehouse and can alter their paths in real time to avoid obstacles, choose the most efficient routes, and adapt to changes in the warehouse layout. AMRs are especially useful in e-commerce fulfillment centers and can work alongside human operators to reduce their workload and enhance productivity.
Automated Sortation Systems
Automated sortation systems automatically identify and sort products on a conveyor system and direct them to various warehouse locations based on specific criteria. As items move along the conveyor, they are identified using barcode scanners, RFID readers, or optical recognition technologies. Once identified, systems tilt, pivot, push, or drop items to divert them where they need to go.
Automated sortation systems can process thousands of items per hour, making them a critical component of smart warehouses. This rapid processing capability is essential in high-volume environments like e-commerce fulfillment centers, where customer orders must be processed quickly to meet delivery expectations.
Collaborative Robots
Collaborative robots (or cobots) are designed to assist human workers, in taking on repetitive, strenuous, or precision-required tasks, such as picking, packing, and palletizing. This allows human workers to focus on more complex, value-added activities that require human skills like problem-solving, quality control, maintenance, and supervision.
Goods-to-Person Technologies (GTP)
Instead of workers moving to and from various locations to collect items (a traditional method known as “person-to-goods”), goods-to-person technologies bring the items directly to the workstation where a person is stationed. GTP systems typically use a combination of automated storage and retrieval systems, conveyors, and robotic shuttles to retrieve items and deliver them to a fixed station. Workers remain at their stations and focus on value-added tasks, which optimizes safety and productivity.
Wearable Technology
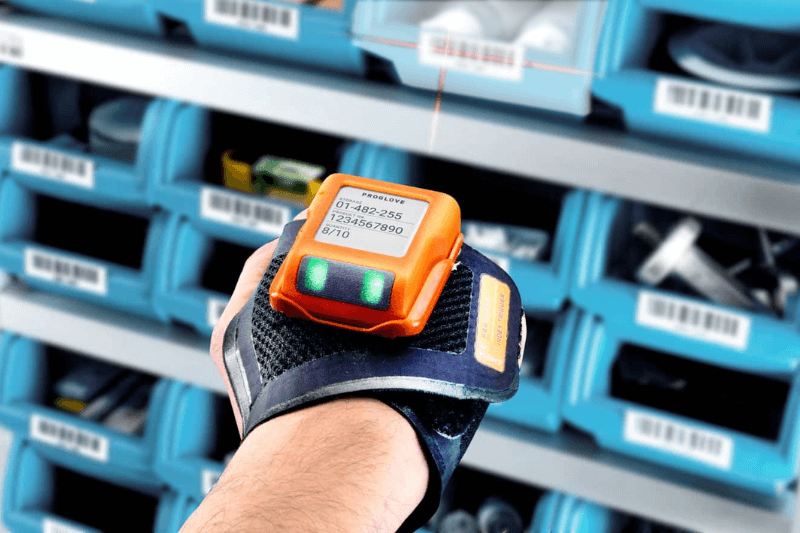

Smart warehouses are embracing wearable technologies to empower their human workforce by enhancing worker mobility. These devices free up workers’ hands and integrate seamlessly with warehouse management systems to provide employees with direct access to system data and real-time guidance for faster and more accurate order processing. One great example of wearable technology in smart warehouses is wearable barcode scanners.
Wearable barcode scanners, like those offered by ProGlove, significantly enhance the efficiency and precision of warehouse tasks. These ergonomic devices allow workers to access crucial information and perform scanning tasks on the go, anywhere within the warehouse. By integrating wearable scanners into daily operations, smart warehouses can streamline workflows, reduce the time spent on manual data entry, and increase the accuracy of inventory tracking and order processing.
Warehouse Augmented Reality (AR)
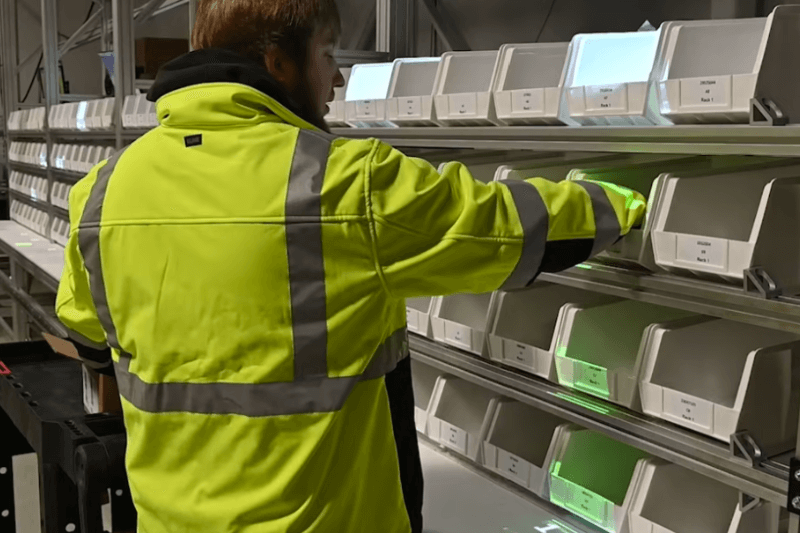

Imagine warehouse workers receiving real-time instructions and guidance, overlaid directly onto their physical environment, as they move through the facility. Warehouse AR empowers workers by superimposing digital information, like picking instructions and inventory location, onto the physical world, improving key material handling tasks for speed and accuracy.
Using AR for visual guidance empowers warehouse workers in several ways:
- Enhance efficiency and accuracy: AR technology can map out the most efficient and safe routes for warehouse personnel. By precisely highlighting the location of items within the warehouse and offering detailed pick-and-place guidance, AR minimizes wasted time, reduces the potential for errors, and speeds up order fulfillment.
- Optimize material handling workflows and picking routes: From receiving to shipping, projected AR technology can guide warehouse associates through stowing, picking, packing, and staging activities.
- Efficient shipping dock staging: AR guidance optimizes the staging process at shipping docks, ensuring that goods are systematically organized in the right sequence and ready for transport.
- Reduce cognitive load and worker stress: 79% of warehouse workers are concerned about managing workloads and high stress levels. AR frees up mental space for workers, allowing them to concentrate more fully on the task at hand. This reduction in cognitive load leads to less fatigue, fewer errors, and greater overall job satisfaction.
- Enhance worker safety: AR enhances worker safety in warehouses by providing real-time hazard alerts and safe path guidance. By integrating with warehouse systems and vehicle sensors, AR offers proximity alerts and collision prevention, guiding workers along safe routes and helping them avoid high-traffic areas.
FREE DOWNLOAD: Your Guide to Warehouse Augmented Reality [Access Now]

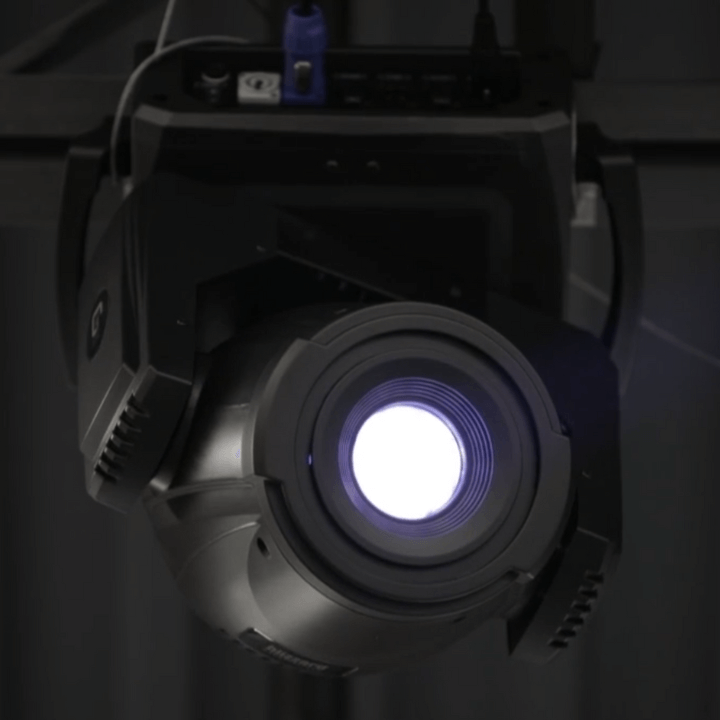
LightGuide SpotGuide AR: An Example of Warehouse AR in Action
LightGuide’s SpotGuideAR platform is a prime example of how augmented reality can optimize warehouse operations. This AR technology integrates seamlessly with ProGlove’s wearable barcode scanners, creating a powerful combination for optimized material handling.
Using advanced projection technology, LightGuide AR visually directs workers to specific locations within the warehouse. Simultaneously, ProGlove’s wearable scanners deliver critical information like part numbers, quantities, and storage locations directly to workers’ hands. This combined approach ensures workers have the right information, exactly where they need it.
Additionally, LightGuide AR software integrates with 3D sensors to confirm bin selections and provides haptic feedback through ProGlove wearables—a subtle vibration alerts the user if an incorrect bin is reached, preventing errors and further refining workflows.
The Human Element in Smart Warehousing
The rise of warehouse automation might lead some to believe that human workers are becoming obsolete. However, a key finding from Zebra Technologies’ Warehousing Vision Study reveals a different reality:
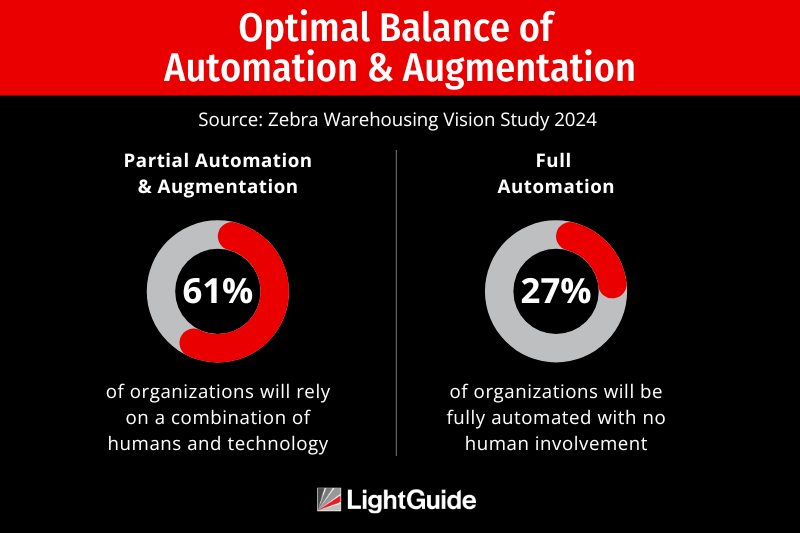
While 27% of decision-makers plan to utilize full automation by 2024, the majority (61%) will rely on a human-machine collaboration approach. This finding highlights a future where technology augments human capabilities, rather than replaces them.
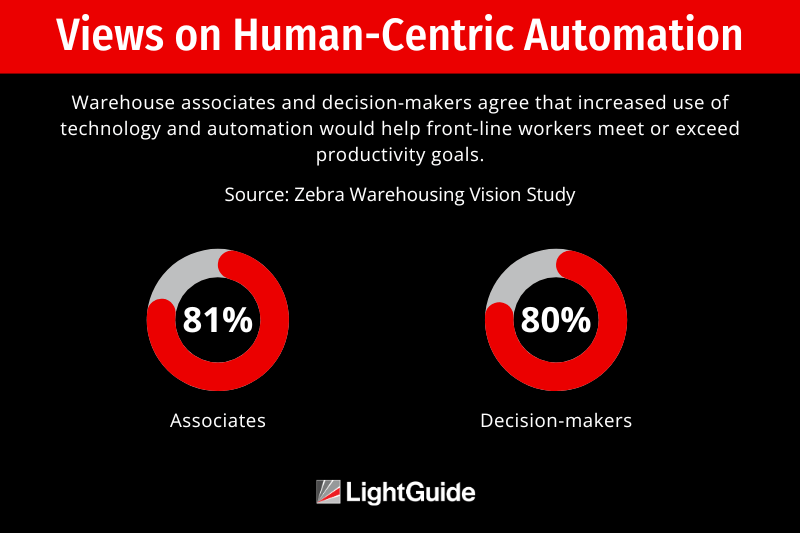
The study also found a strong alignment between warehouse associates and decision-makers regarding the role of technology. A staggering 73% of decision-makers stated that providing frontline workers with technology is a top priority, and 83% of warehouse workers reported feeling more empowered with access to technology and automation.
As you can see, warehouse automation isn’t simply about replacing workers – it’s about empowering them with the tools they need to thrive. By fostering a collaborative environment and strategically planning their workforce, smart warehouses can use the strengths of both humans and technology. Let’s explore how this is achieved:
- Human-machine collaboration: While robots excel at repetitive tasks, humans bring critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills to the table. Human workers can handle exceptions, manage unexpected situations, and ensure smooth operation of automated systems.
- Augmenting human capabilities: Technology acts as a force multiplier for human capabilities. Augmented reality and wearable devices can enhance worker productivity and safety by providing hands-free access to information and instructions. Additionally, AI-powered tools can help with complex tasks, allowing workers to focus on higher-level activities.
- Strategic workforce planning: Automation doesn’t eliminate the need for human workers, it simply changes the types of roles needed. Strategic workforce planning allows warehouses to identify tasks best suited for automation and those that require human capabilities.
Benefits of Smart Warehousing
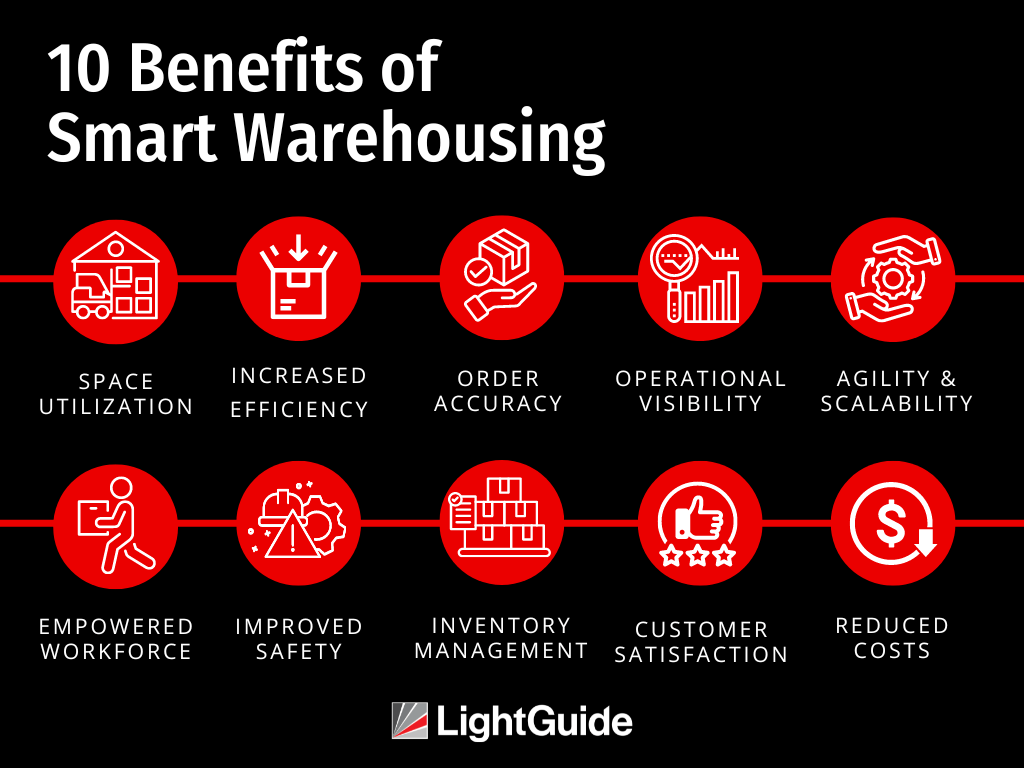
Implementing smart warehouse technologies and strategies creates a competitive advantage for businesses in the fast-paced logistics landscape. This is achieved through many benefits, including greater efficiency, accuracy, and responsiveness.
#1 Better Space Utilization
Every square foot in a warehouse is valuable real estate. Smart warehouses use intelligent storage solutions and optimized layouts to maximize space utilization. High-bay racking systems and vertical storage carousels allow for efficient storage of goods in a condensed footprint.
Additionally, warehouse management systems can analyze historical data and product characteristics to optimize picking routes and item placement, minimizing wasted space and travel time for warehouse workers. By maximizing space utilization, smart warehouses can store more inventory without expanding their physical footprint, reducing storage costs and improving overall efficiency.
#2 Increased Operational Efficiency
Traditional warehouses, lacking smart technologies, see a significant portion of daily operations consumed by picking, packing, and shipping tasks. These manual processes can be time-consuming and prone to errors, with a significant portion of picking time wasted on travel between locations.
Research by Amware Fulfillment reveals: Travel time is the enemy of efficient order picking. It can account for up to half the total picking time and delay order fulfillment.
By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining workflows, smart warehouses minimize wasted time and effort for warehouse associates, resulting in faster order fulfillment, higher on-time delivery rates, and lower operating expenses.
#3 Error Reduction
Warehouses are full of intricate processes, each with the potential for errors. According to a survey of 200 retailers from inventory management technology provider Stitch Labs, two-thirds (63%) of inventory or fulfillment issues are caused by human error from manual process management.
Material handling is especially prone to mistakes. Picking errors, which cost an average of $20-60, can quickly add up and erode profitability over time. Research suggests businesses spend 20% of their operational budget addressing and rectifying human errors.
Smart warehouses minimize these errors by using advanced technologies and automation to empower workers. Real-time data on inventory levels and product locations guide workers through the fulfillment process, ensuring accurate selections.
#4 Enhanced Operational Visibility for Better Decision-Making
Smart warehouses use a network of sensors, RFID tags, and other interconnected technologies to provide real-time data and insights into inventory levels, labor performance, and overall warehouse operations. This transparency empowers better decision-making about warehouse operations, resource allocation, and overall inventory management strategies.
#5 Greater Agility and Scalability
Data-driven insights allow smart warehouses to anticipate demand fluctuations and adapt their operations, leading to faster response times and improved customer satisfaction.
#6 Empowered Workforce
By implementing collaborative automation and augmentation technologies, smart warehouses can streamline repetitive and physically demanding tasks. This frees up valuable human potential, allowing workers to focus on higher-value activities that require critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Examples include managing complex orders, overseeing fulfillment processes, and ensuring quality control. This shift empowers workers, fosters engagement, and contributes to a more efficient and adaptable warehouse operation.
#7 Improved Safety
Smart warehouses significantly improve worker safety, a critical concern in an industry where the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported approximately 5.5 workplace injuries per 100 full-time employees in 2021. Here’s how:
- Data-driven safety enhancements: Smart warehouses use data analytics to monitor and analyze workplace conditions. By identifying patterns and pinpointing areas with high accident risks, managers can proactively implement changes to workflows and processes. This might include rearranging the warehouse layout to reduce congestion or modifying task assignments to limit exposure to hazardous conditions.
- Robotics for hazardous tasks: Robotics play a pivotal role in reducing the physical strain on human workers by taking over strenuous and repetitive tasks. For example, robots can handle heavy lifting, moving, and sorting of goods, which are common sources of injury in traditional warehousing environments.
- AR-guided picking routes: AR systems project visual warnings and barriers directly in workers’ fields of vision, highlighting dangers like moving forklifts and AMRs.
#8 Effective Inventory Management
The rise of e-commerce has amplified the need for accurate inventory management. The data visibility afforded by smart warehouse systems allows suppliers to provide accurate, real-time information to customers about product availability. Furthermore, these systems can leverage historical sales data and analytics to predict future demand and minimize stockouts.
#9 Higher Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
Timely and accurate order fulfillment leads to higher satisfaction. This reliability attracts repeat business, drives positive reviews, and increases sales, directly boosting profitability.
#10 Reduced Operating Costs
Minimizing warehouse operational costs requires a strategic approach that uses innovative technology and skilled human resources. Smart warehouses deliver on this by optimizing processes at every stage. Intelligent systems minimize errors and non-value-added efforts, while optimized warehouse layouts maximize space utilization, reducing the need for more square footage.
By combining human ability with intelligent automation, smart warehouses improve resource allocation and reduce overall operational expenses, allowing businesses to focus on growth and profitability.
Looking Forward: The Future of Smart Warehousing
The future of warehousing is undoubtedly smart, using intelligent and interconnected systems to create a more efficient, adaptable, and customer-centric supply chain.
Fueled by rapid technological advancements and changing market demands, smart warehousing will continue to evolve. Further advancements in robotics and augmented intelligence will push the boundaries of efficiency and responsiveness, enabling intelligent inventory management and order fulfillment. These innovations will allow smart warehouses to achieve faster order fulfillment, improved accuracy, and a stronger competitive edge.
By embracing change, investing in the right technologies, and upskilling their workforce, warehouse leaders can remain competitive in the fast-paced world of on-demand fulfillment.

Ready to Revolutionize Your Warehouse with Cutting-Edge Technology?
Contact us today to explore the transformative power of LightGuide’s warehouse AR solutions.