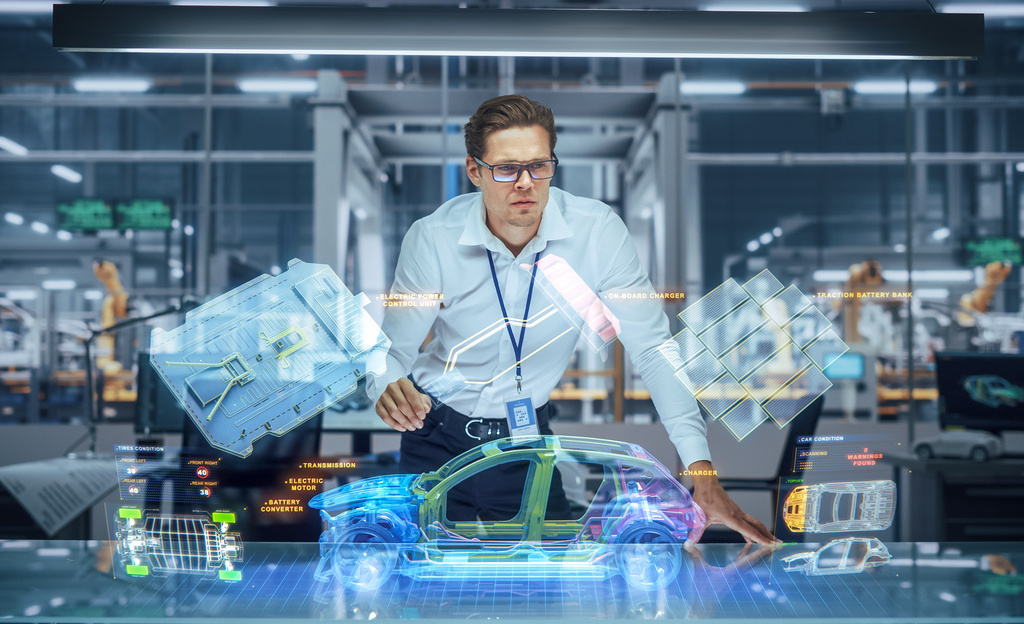
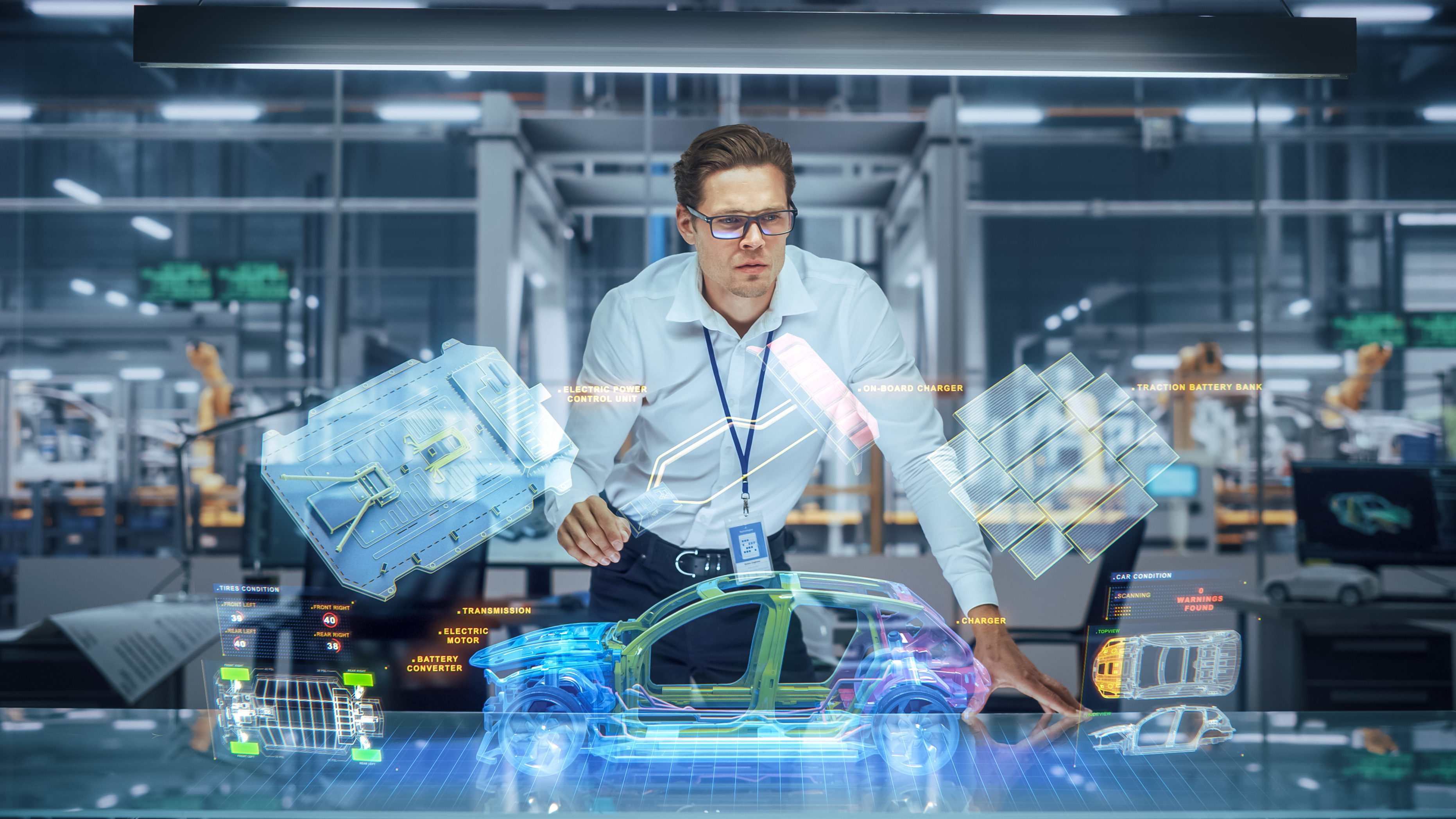
In recent years, manufacturers have made enormous strides, proving they have the innovation and resilience to handle future disruptions and changing demands on their business. Manufacturers are successfully navigating a variety of manufacturing technology trends while building up to Industry 4.0 connectivity standards. Some pioneers are even propelling their factories forward to embrace Industry 5.0, maximizing the collaboration between humans and smart systems
How can we accelerate these positive shifts in 2023? Here’s a look at the top six manufacturing trends of 2023 that will shape our factories of the future.
The Top 6 Manufacturing Technology Trends
1. Accelerated Digital Transformation
Not only are transformative technologies expanding and upgrading, they are starting to work in conjunction with each other. There are many new tools at our disposal, like artificial intelligence and machine learning, cloud computing, and augmented reality (AR). As these tools became mainstream and the qualifiers for a “factory of the future,” manufacturers originally assumed that they worked singularly, contributing only one key benefit.
However, these technologies weren’t meant to work alone. Recognizing and exploiting their collective range of benefits propels their long-term nature and fully unlocks what they offer. For example, AR and cloud computing are unlocking new ways to view and access data at an enterprise-level. LightGuide’s augmented reality software platform is capable of this, connecting to third party data dashboards like Microsoft’s Power BI and Siemen’s MindSphere to display digitally collected manual process data.
The convergence of these technologies are also driving the advancement of the digital twin for manufacturing; a near real-time digital image of a physical object or process that helps optimize business performance.
RELATED: An Overview of the Digital Twin in Manufacturing
2. Data and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
Dramatic increases in the use of interconnected devices in industrial environments allow manufacturers to collect valuable data—data that can provide insights to optimize their factories.
Today, manual processes are more easily tracked. By using leading industry tools like AR, manufacturers get real-time views into individual workstation inputs, factory-level efficacy, and enterprise-level performance. Being able to see the progression of operational performance over three levels delivers unprecedented insight that manufacturers then leverage for greater decision-making.
Additionally, the IoT data that innovative manufacturing technologies collect provides insight into the functionality of tools. Manufacturing technologies with predictive maintenance capabilities provide insight into the system itself. They track the lifetime of a system, preventing outages by giving usage reports before system failures and extending the lifetime of equipment.
3. Expanding Augmented Reality
Although manufacturing has become an extremely tech-focused industry, it is important to know that 72% of factory tasks are still performed by humans. Due to that, we need to acknowledge that our continued innovation must support our workers.
Augmented reality is the key to bridging the gap between man and machine. It is a highly innovative, proven technology that assists workers throughout their tasks. By displaying visual and auditory cues in an individual’s surroundings, augmented reality enhances a workers experience and performance, guiding them through complex tasks for the greatest efficiency and productivity.
Guiding and tracking manual processes, AR leads to a new understanding of our operations. Leading manufacturers are still using automation to handle simple, repetitive tasks. But, by pairing AR with automation, “AR interfaces can blend in the working environment and enrich it, making the interaction with [robots] natural and intuitive,” according to a study at the University of Patras.
Considering the future of manufacturing, augmented reality is the perfect stepping stone. It simultaneously brings manufacturers to Industry 4.0 standards while accelerating their digital transformation into the people-centric elements of Industry 5.0.
RELATED: Augmented Reality Applications on the Factory Floor eBook
4. Reskilling the Workforce
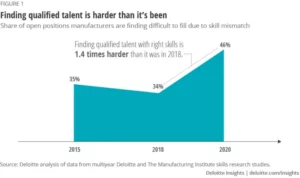
Drastic expansions to the digital intelligence of the manufacturing industry require a heightened set of worker skills. Unfortunately, with long, partial training programs, flawed comprehension of job expectations, and fewer workers available to evolve into middle-skill jobs, it’s hard to find skilled talent ready to start on the line quickly—in any role. Due to this, reskilling strategies have expanded.
While some licensing and certification programs can take months or years to complete, manufacturers rarely have that time to wait when they need to meet today’s deadlines. A report from Deloitte noted that “without making changes to the skills composition of the workforce, manufacturers could leave up to 2.1 million jobs unfilled between 2020 and 2030, impacting everything from productivity to innovation and competitiveness to GDP.”
Groups like MxD have released free hiring guides to aid companies in identifying and filling the roles they need. In other instances, companies have adopted rotational programs to ease redeployment of workers to different roles. Some new technologies are helping manufacturers bridge the skills gap. The use of AR can accelerate training and reduce disruptive training variance.
RELATED: How to Use Augmented Reality to Upskill Workers
5. The Rise of Reshoring
Manufacturers are not only constructing state-of-the-art factories of the future, but they are making sure they are future-proof as well. The COVID-19 pandemic showed us how easily the supply chain can change. Since then, it has been pertinent to keep a close eye on our supplies and distribution, making reshoring a top priority.
Since 2010, over 757,000 jobs were brought back to the U.S. from foreign countries. Over the last few years, manufacturers have showed a heightened interest in continuing to reshore jobs. According to Kearny, the U.S. made positive progress towards reshoring from 2018 to 2019, dropping the manufacturing import ratio from 13.06% in 2018 to 12.08% in 2019.
On top of that, a report from Thomas for Industry found that 54% of manufacturers shared high interest in reshoring in 2020 and that interest increased to 83% in 2021.
Despite those positive trends, outsourcing has risen. The manufacturing import ratio rose to nearly 14.5% in 2021.
By bringing work back to the U.S., manufacturers experience an expansive range of benefits:
- Transportation is more timely and less expensive
- Supportive infrastructure is already in place and easier to build
- Assistive and automated technology is more abundant in the U.S., supporting processes that were previously prone to human error
- Labor and wage costs are increasing overseas

6. Actionable Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
Two-thirds of the manufacturing industry are male. Nearly 70% are white. In an age of complete industrial transformation, it is imperative that manufacturing is inclusive and accessible for all people. Businesses will accelerate DEI initiatives in 2023. Eliminating the barriers that prevent fair access, opportunity, and resources for all employees will have dramatic, positive impacts across the enterprise.
According to research by Deloitte, women are nearly two times more likely to leave the industry than men, primarily because of a lack of work/life balance and flexible work arrangements. Acting to create a non-discriminatory, welcoming culture within the workplace is proven to drive business performance and innovation and attract and retain talent.
Tapping into the myriad abilities of people with disabilities can also be part of the solution. According to the 2017 Disability Statistics Annual Report from the Institute on Disability, nearly 1 in 8 people in the U.S. has a disability, and that number increases annually. Companies that succeed in incorporating candidates with disabilities can draw a large and mostly untapped new source of talent.
RELATED ARTICLE: Empowering the Social Economy with AR
Interested in learning more about enabling the latest manufacturing trends in your factory? Send us a message to schedule a consultation with our AR experts.