Your Guide to Improving Intralogistics in the Age of Smart Warehouses

As the global supply chain becomes more complex, more efficient, responsive, and intelligent warehouse solutions are necessary. At the heart of warehouse operations is intralogistics, the process of managing the internal flow of goods and information to drive improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and responsiveness.
Continue reading to explore the key components of intralogistics, discover the technologies that enhance its capabilities, and evaluate the challenges and opportunities of optimizing intralogistics in the age of smart warehousing.
Plus, access our guide to using augmented reality to improve warehouse material handling processes.
IN THIS ARTICLE:
- What is Intralogistics?
- Key Components of Intralogistics
- Why Intralogistics Matters in the Age of Smart Warehouses
- Common Intralogistics Challenges Impacting Warehouse Efficiency
- How to Improve Intralogistics for Smarter Warehousing
- The Role of Technology in Improving Intralogistics
- Benefits of Efficient Intralogistics
What is Intralogistics?
Intralogistics (or internal logistics) involves managing the internal flow of information and goods within a company’s warehouse or distribution center. In facilities with multiple interconnected sites, intralogistics manages the flow between these sites to ensure production lines are adequately supplied.
Key Components of Intralogistics
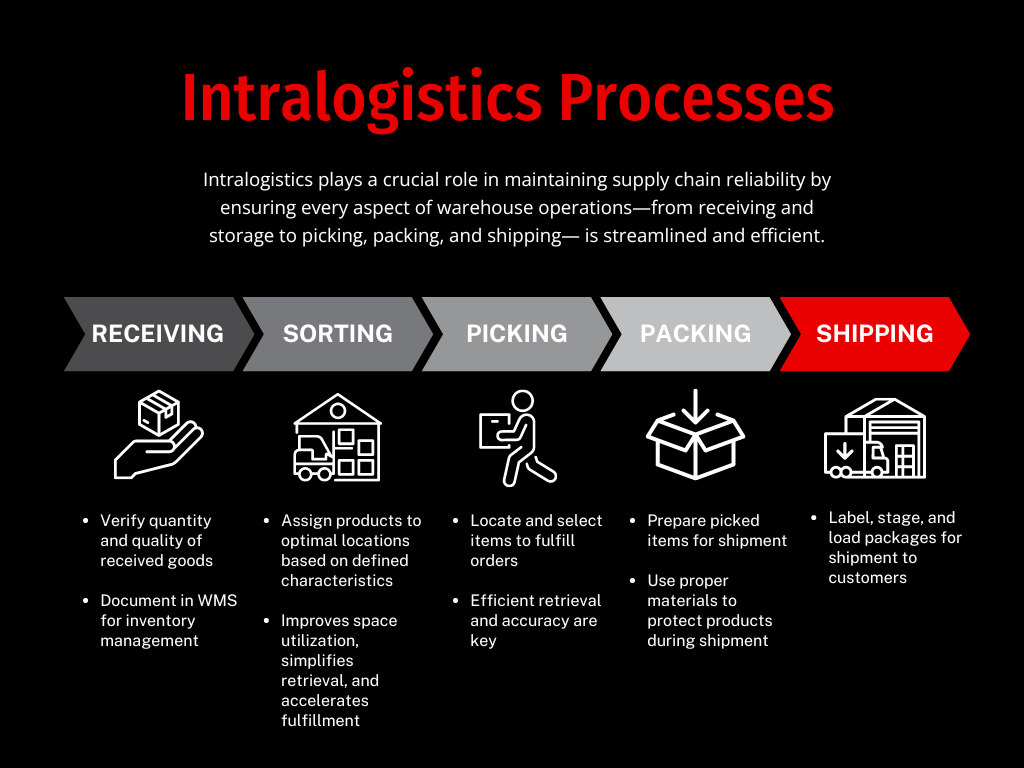
Intralogistics is crucial in maintaining supply chain reliability. It ensures every aspect of warehouse operations is streamlined and efficient. This is accomplished through careful coordination of several key components of intralogistics, including:
Material Handling
Efficient material handling practices are essential for efficient order fulfillment and timely deliveries. Everything from unloading incoming trucks and palletizing them for storage to picking items for orders and packing them efficiently for shipment must be carefully coordinated.
Intralogistics optimizes these material handling processes by:
- Coordinating the strategic placement of goods to streamline picking processes and reduce transit times.
- Organizing goods in a way that maximizes space utilization and simplifies retrieval based on several factors such as product weight, size, and demand.
By optimizing these aspects of material handling, intralogistics ensures warehouses operate at peak efficiency, leading to faster order fulfillment and satisfied customers.
Inventory Management
Intralogistics lays the foundation for data-driven inventory management, where warehouses utilize insights on stock levels, sales trends, and product movement to optimize inventory strategies. This approach minimizes the risk of stockouts and overstocking, improving efficiency and cost savings.
Information Flow
Intralogistics relies on the efficient flow of information to ensure seamless warehouse operations and timely, well-informed decisions. Real-time data and communication systems link various aspects of warehouse operations through embedded sensors and monitoring tools. This provides visibility into critical variables such as inventory levels, order status, and the locations of robots. With the ability to track goods in real-time, warehouses are better equipped to adjust workflows based on demand fluctuations.
Technological Integration
Modern warehouses operate on the foundation of interconnected technology systems, where all components within the warehouse communicate and function cohesively. Intralogistics plays a crucial role in supporting this connectivity.
Why Intralogistics Matters in the Age of Smart Warehouses

As traditional warehouses evolve into smart facilities, the role of intralogistics becomes increasingly important. By optimizing the flow of information and materials through enhanced use of technology, labor, and equipment, intralogistics establishes the groundwork necessary for a fully optimized smart warehouse. This optimization unlocks the full potential of warehouse automation, ensuring resources are utilized effectively and operations are streamlined to meet the demands of modern supply chains. Here’s how:
Enhanced Coordination
Intralogistics ensures warehouse operations are well-coordinated. In a smart warehouse, this coordination is supported by technology and communication systems that connect various aspects of warehouse operations.
Seamless Operations Through Technology
Intralogistics coordinates the flow of goods within the warehouse, while smart technologies enable workers to execute tasks with greater precision and efficiency. For example, an IoT-enabled warehouse management system can dynamically manage inventory based on real-time demand and supply conditions.
Integrated Systems for Streamlined and Cohesive Operations
By integrating technology with intralogistics, warehouses achieve seamless interaction between digital and physical workflows. This unified approach reduces the complexity of managing separate systems and streamlines the execution of tasks. It also ensures warehouses operate at peak efficiency, with minimal waste and enhanced throughput.
Real-Time Monitoring and Control
Smart warehouse technologies provide real-time monitoring and control capabilities that enhance intralogistics. For example, sensors and tracking systems can monitor the condition and flow of goods. As a result, intralogistics can be dynamically adjusted for workflow optimization.
Data-Driven Resource Allocation for Agile Operations
Smart warehouses automate data collection and analysis across various operations. Intralogistics uses this information to optimize resource allocation and dynamically adjust workflows. This ensures operations can quickly adapt to changes in demand, supply disruptions, or operational bottlenecks, minimizing downtime and maintaining steady throughput.
Predictive and Proactive Management
Combining machine learning with intralogistics enhances the proactive capabilities of warehouse operations. For example, predictive insights can inform inventory decisions, labor allocation, and maintenance schedules before issues arise.
Enhanced Scalability
Intralogistics enables facilities to expand operations or adjust capacities with minimal disruption. This flexibility is crucial for accommodating seasonal fluctuations, market growth, or changes in business strategy.
Common Intralogistics Challenges Impacting Warehouse Efficiency
The dynamic nature of modern supply chains presents new hurdles for intralogistics. Fluctuating customer demands and evolving product lines mean warehouses must adapt operations to stay competitive. However, traditional intralogistics methods often struggle to keep pace with rapid changes.
Supply Chain Complexity
More SKUs, shorter product life cycles, and the need for customized logistics solutions add pressure on intralogistics systems to be more versatile and responsive. Warehouses must be able to adapt operations swiftly based on seasonal fluctuations, market growth, or changes in product offerings.
Visibility and Tracking
Traditional methods struggle to provide real-time visibility into inventory levels and the location of goods within the warehouse. This lack of transparency can make it difficult to react quickly to changes in demand. It also hinders the ability to optimize picking routes and warehouse layout, further contributing to picking and packing errors.
Technological Integration Challenges
As warehouses implement technologies to keep pace with change, integrating new systems with existing infrastructure can be complex. This includes difficulties in data synchronization, software compatibility, and maintaining workflow continuity during upgrades.
Labor Skills Gap
The shift toward more technologically advanced warehouse systems requires the workforce to acquire additional skills. There is often a gap between the existing skills of warehouse staff and the new capabilities needed to manage and operate sophisticated warehouse systems.
Inefficient Space Utilization
Traditional methods may fail to optimize the warehouse layout for maximum storage and optimal flow of goods, leading to slow order fulfillment.
Sustainability Challenges
Increasingly, businesses are expected to operate sustainably. Reducing waste and optimizing energy use without compromising efficiency can be challenging.
Regulatory and Compliance Pressures
Compliance with ever-changing regulations can complicate intralogistics. This includes environmental regulations, safety standards, and customs requirements, which vary widely across regions and impact how goods are stored and handled.
Cybersecurity Risks
As intralogistics relies more on interconnected systems, the risk of cyber threats increases. Protecting data and ensuring the security of automated systems become critical challenges.
How to Improve Intralogistics for Smarter Warehousing

The competitive landscape of logistics demands warehouse efficiency. Intralogistics, which controls the management of goods and information flow within a warehouse, plays a significant role in achieving this. Here are some steps warehouse managers can take to overcome common intralogistics challenges and pave the way for smarter, more responsive operations.
Enhance Data Analytics Capabilities
Modern warehouses can leverage data to identify patterns and trends that inform process improvements. Machine learning algorithms can then be applied to predict future demand, leading to better inventory management and resource allocation. This data-driven approach forms a robust foundation for smarter, more efficient warehouse operations and equips businesses to meet modern supply chain demands with greater agility.
Foster Continuous Improvement and Innovation
Continuously review and adjust processes based on feedback and operational data. Regularly evaluating and adjusting processes ensures intralogistics remain adaptable and efficient in the ever-evolving logistics landscape.
Optimize Warehouse Layout and Design for Improved Flow and Space Utilization
A well-designed warehouse layout is essential for efficient intralogistics. By strategically placing materials within the warehouse, intralogistics can optimize the storage and retrieval of goods to improve material flow and worker productivity. For example, zone picking and batch picking strategies minimize picker travel time by grouping similar items in designated zones. Additionally, incorporating ergonomic principles into workstation design minimizes worker fatigue and the risk of injuries. Together, these efforts create a streamlined and worker-friendly environment that accelerates order fulfillment and increases productivity.
Leverage Technology for Smarter Warehousing
Technology plays a pivotal role in providing real-time visibility and tracking capabilities, which are essential for optimizing warehouse workflows. By implementing strategic technology solutions, warehouse managers can improve several key components of intralogistics including:
- Automating repetitive and physically strenuous tasks
- Streamlining storage and retrieval processes
- Optimizing material handling for accuracy and speed
- Enhancing visibility and control over inventory management
- Gaining instant insights into equipment performance and worker productivity
Focus on People with Effective Training and Change Management
While technology plays a vital role in modern intralogistics, optimizing operations goes beyond implementing new systems. Empowering the human workforce and fostering a culture of continuous improvement is equally crucial for success. Invest in comprehensive training programs to ensure staff are proficient with technologies and processes. Implementing a clear change management process can help address concerns, reduce resistance, and enhance adoption rates. These efforts enhance operational capabilities and foster a culture of learning. By prioritizing both technology and human capital, warehouses can create a truly intelligent and responsive intralogistics system.
Implement a Phased Approach to Technology Integration
Plan your technology integration in phases. Start with core systems and gradually integrate other solutions as your team builds expertise. Additionally, partner with experienced technology providers who can ensure seamless integration and data synchronization.
A Closer Look at the Role of Technology in Improving Intralogistics

Intralogistics is significantly enhanced by advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and collaborative automation. These technologies enable workers to execute tasks with greater precision and efficiency by fusing digital and physical aspects of warehouse operations. This transforms traditional practices into highly efficient, data-driven processes that streamline operations and enhance decision-making.
Here are just some of the smart warehouse technologies being used to enhance intralogistics:
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Play a crucial role in coordination by dynamically managing inventory levels and providing real-time data on stock movement and worker productivity.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Enable real-time tracking of goods and equipment to enhance visibility and contribute to proactive management of the warehouse environment.
- Robotics and Automation: Technologies like automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS), autonomous mobile robots, and intelligent sortation systems streamline repetitive and physically demanding storage and retrieval processes to increase efficiency and minimize errors.
- Big Data and Machine Learning: Help predict demand, optimize resource allocation, and improve operational decisions by analyzing historical data and real-time inputs.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Warehouse augmented reality empowers workers by superimposing digital information onto the physical world, optimizing key material handling tasks for speed and accuracy.
RELATED ARTICLE: Smart Warehousing Technologies: A Comprehensive Guide

Benefits of Efficient Intralogistics
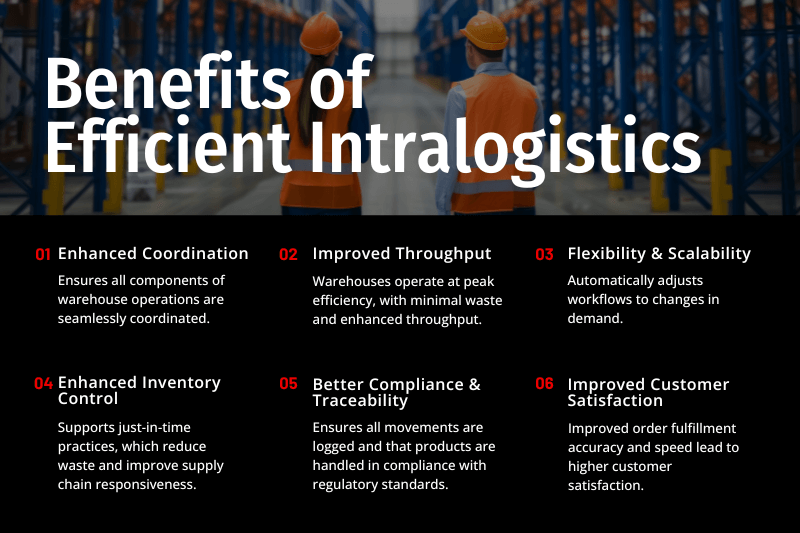
Improved Throughput
Efficient intralogistics leads to improved throughput. Automated systems like conveyors, automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), and sortation systems streamline the movement of goods through the warehouse, reducing bottlenecks and delays. This expedites the flow of products from receiving to shipping, which is crucial for meeting customer demands and tight delivery schedules.
Enhanced Inventory Control
Advanced WMS and IoT devices provide real-time inventory data. This reduces excess inventory and out-of-stock situations, ensuring capital isn’t tied up unnecessarily and that supply meets demand. Better inventory control supports just-in-time inventory practices, reducing waste and improving supply chain responsiveness.
Increased Flexibility and Scalability
Efficient intralogistics allow warehouses to quickly adapt to changes in demand and provide businesses with the flexibility to handle peak periods like holiday seasons effectively.
Better Compliance and Traceability
Intralogistics improve compliance with regulatory requirements, particularly in industries where traceability of products is essential. Integrated systems ensure all movements are logged and products are handled in compliance with the standards.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
The accuracy and speed of order fulfillment improve when intralogistics processes are streamlined. Reliable and quick service builds customer trust and can lead to repeat business, which is vital in today’s competitive market.
Are You Prepared for the Future of Intralogistics and Warehouse Management?
Intralogistics is not just a component of modern warehousing—it’s the backbone that supports the entire operation of smart warehouses. As technology evolves, so will intralogistics, becoming smarter, faster, and more interconnected. Integrating advanced technologies with comprehensive management strategies ensures warehouses are efficient and cost-effective.
As technology and market demands evolve the ability to adapt and improve intralogistics will become increasingly important in maintaining competitive advantage. Improving intralogistics can help businesses ensure they are ready to meet the global logistics challenges of today and tomorrow.

Ready to Explore Warehousing Solutions?
Connect with our team to see how the LightGuide AR platform can enhance material handling processes for improved intralogistics.



